Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health. It’s an essential nutrient that our bodies need to function properly. From supporting the immune system to promoting healthy skin and eyes, vitamin E offers a wide range of benefits. In this article, we’ll explore everything you need to know about vitamin E, including its benefits, sources, recommended daily intake, and potential side effects.
Table of Contents
What is Vitamin E?
Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health. It is a group of eight fat-soluble compounds, including four tocopherols and four tocotrienols, that protect the body from oxidative stress and damage caused by free radicals. These free radicals are unstable molecules that can harm cells, leading to aging and various diseases.
Benefits of Vitamin E
- Skin Health: Vitamin E is widely known for its skin benefits. It helps in keeping the skin moisturized, reduces scars, and fights signs of aging like wrinkles. It also protects the skin from damage caused by ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun.
- Immune System Support: Vitamin E boosts the immune system by helping the body fight off infections. It enhances the function of immune cells, making it easier for the body to fend off bacteria and viruses.
- Heart Health: By acting as an antioxidant, Vitamin E helps prevent the oxidation of cholesterol, which can lead to clogged arteries. This helps in maintaining good heart health and reducing the risk of heart diseases.
- Eye Health: Vitamin E is essential for eye health. It helps prevent age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and cataracts, which are common causes of vision loss as we age.
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Vitamin E has anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce inflammation in the body, making it beneficial for conditions like arthritis.
Sources of Vitamin E
Vitamin E can be found in a variety of foods, including:
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, sunflower seeds, and hazelnuts are rich sources of Vitamin E.
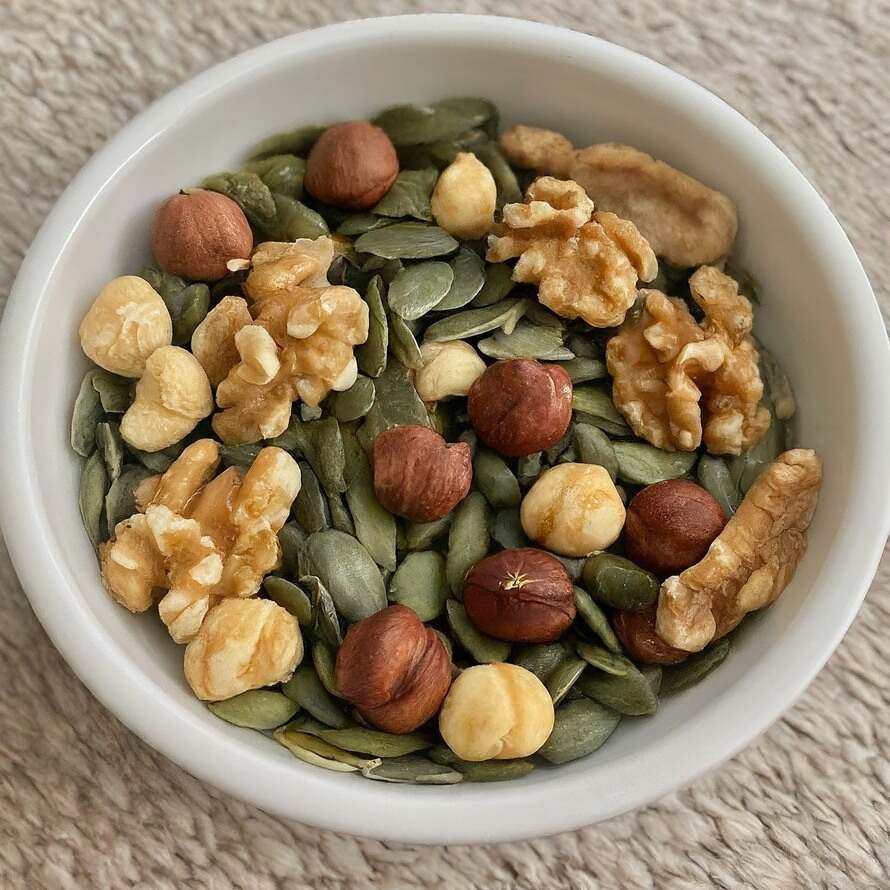

- Vegetable Oils: Sunflower oil, safflower oil, and wheat germ oil are excellent sources.
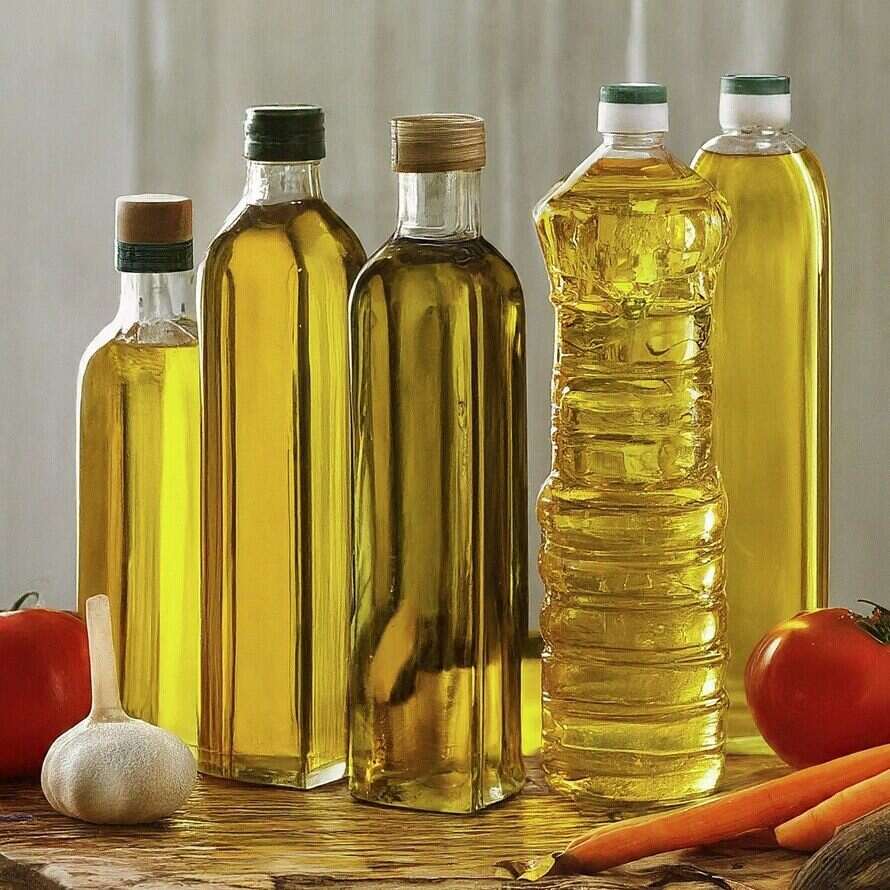

- Green Leafy Vegetables: Spinach, broccoli, and kale contain significant amounts of Vitamin E.
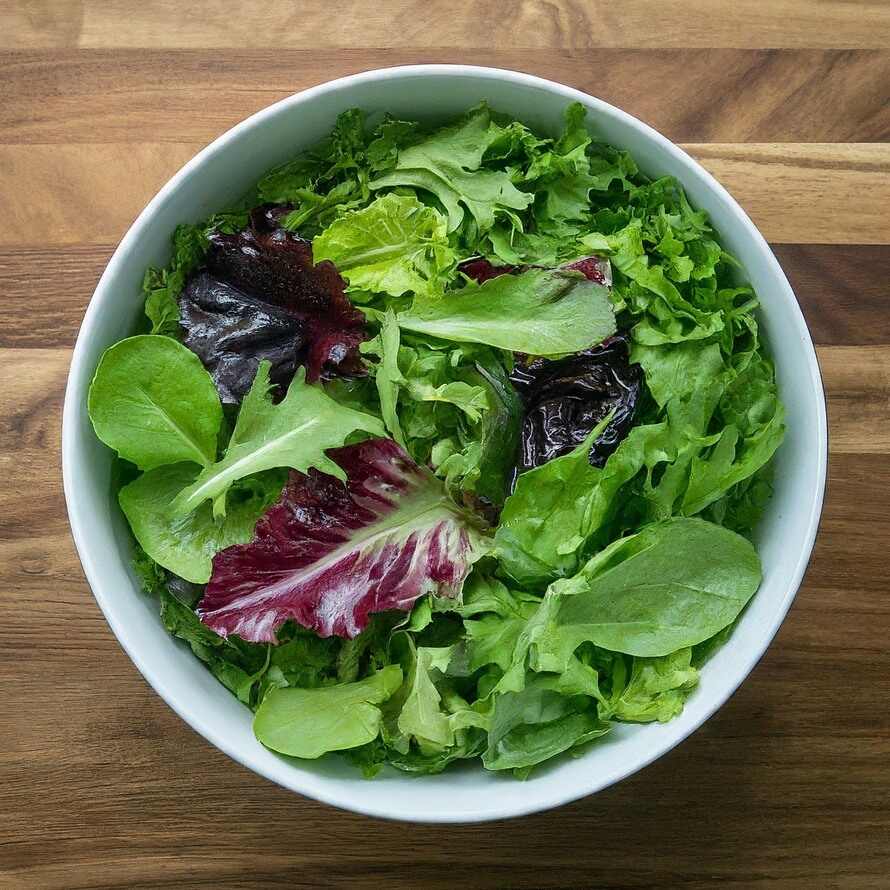

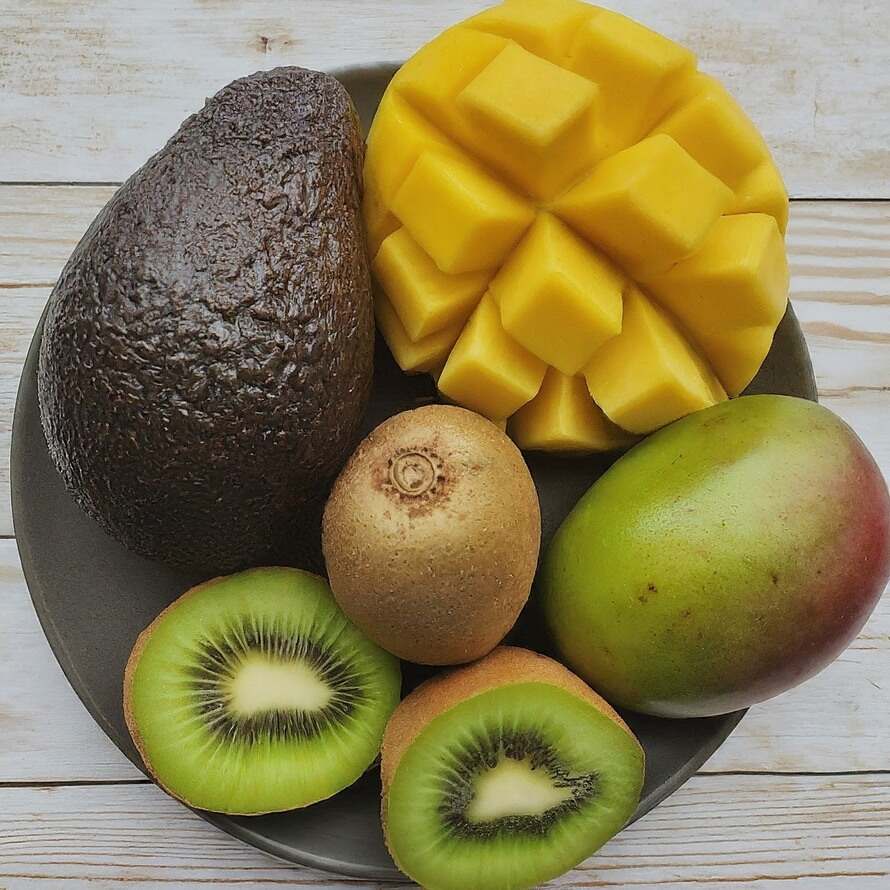
- Fruits: Avocados, kiwis, and mangoes are good sources of this vitamin.

How Much Vitamin E Do You Need?
Vitamin E is essential for maintaining overall health, but how much you need depends on your age, gender, and overall health condition. The recommended daily intake (RDI) of Vitamin E is expressed in milligrams (mg) or international units (IU). For most healthy adults, the RDI is as follows:
- Infants (0-6 months): 4 mg (6 IU)
- Infants (7-12 months): 5 mg (7.5 IU)
- Children (1-3 years): 6 mg (9 IU)
- Children (4-8 years): 7 mg (10.5 IU)
- Children (9-13 years): 11 mg (16.5 IU)
- Teens (14-18 years): 15 mg (22.5 IU)
- Adults (19 years and older): 15 mg (22.5 IU)
- Pregnant Women: 15 mg (22.5 IU)
- Breastfeeding Women: 19 mg (28.5 IU)
These amounts are typically met through a balanced diet that includes Vitamin E-rich foods like nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils. If you follow a diet that is low in fat or you have certain medical conditions that affect nutrient absorption, you may need to monitor your intake more closely.
Vitamin E Deficiency
Vitamin E deficiency is rare in healthy individuals, primarily because Vitamin E is widely available in many foods. However, certain conditions can lead to a deficiency, which can have significant health consequences.
Causes of Vitamin E Deficiency
- Fat Malabsorption Disorders: Since Vitamin E is fat-soluble, any condition that affects the absorption of fats can lead to a deficiency. This includes conditions like Crohn’s disease, cystic fibrosis, and certain liver diseases.
- Genetic Disorders: Rare genetic disorders, such as abetalipoproteinemia, can impair the absorption of Vitamin E from the diet.
- Premature Birth: Infants born prematurely, particularly those with very low birth weight, may not have enough Vitamin E stores and might require supplementation.
Symptoms of Vitamin E Deficiency
- Muscle Weakness: Vitamin E is essential for maintaining muscle health, and a deficiency can lead to muscle weakness or atrophy.
- Vision Problems: A lack of Vitamin E can affect the retina, leading to vision issues such as blurred vision or difficulty seeing in low light.
- Immune System Impairment: Without adequate Vitamin E, the immune system may be weakened, making the body more susceptible to infections.
- Neurological Issues: Severe deficiency can cause nerve damage, leading to problems with coordination and movement, as well as tingling or numbness in the limbs.
Vitamin E Supplements
Vitamin E supplements are available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and oils. While it’s generally best to get nutrients from food, supplements can be helpful in certain situations, especially for those at risk of deficiency.
Types of Vitamin E Supplements
- Natural vs. Synthetic:
- Natural Vitamin E (d-alpha-tocopherol): This form is derived from natural sources like vegetable oils and is more biologically active, meaning it’s more easily absorbed by the body.
- Synthetic Vitamin E (dl-alpha-tocopherol): This form is made in the lab and is less potent than the natural version, so higher doses may be needed to achieve the same effect.
- Mixed Tocopherols: Some supplements include a mix of different types of tocopherols (alpha, beta, gamma, and delta) to provide a broader range of antioxidant benefits.
- Oil-Based vs. Dry Form:
- Oil-Based Capsules: These are the most common form of Vitamin E supplements, typically preferred because Vitamin E is fat-soluble and requires fat for proper absorption.
- Dry Form (Non-Oil Based): These are usually recommended for people who have trouble digesting fats or have fat malabsorption issues.
Benefits of Vitamin E Supplements
- Filling Nutritional Gaps: Supplements can help individuals who have trouble getting enough Vitamin E from their diet, such as those on low-fat diets or with absorption issues.
- Supporting Specific Health Conditions: Vitamin E supplements may be recommended to support conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, where oxidative stress plays a role.
- Skin Health: Vitamin E is often taken or applied topically for its skin benefits, helping to reduce the appearance of scars and promoting healing.
Risks and Side Effects of Vitamin E Supplements
While Vitamin E is generally safe when taken within recommended amounts, excessive intake can lead to adverse effects. The tolerable upper intake level (UL) for Vitamin E is 1,000 mg (1,500 IU) per day for adults. Exceeding this amount can result in:
- Increased Bleeding Risk: High doses of Vitamin E can interfere with blood clotting, leading to an increased risk of bleeding, particularly in people taking blood-thinning medications.
- Nausea and Diarrhea: Some people may experience digestive issues if they take too much Vitamin E.
- Fatigue and Weakness: In rare cases, excessive Vitamin E intake can cause muscle weakness, fatigue, or other symptoms of toxicity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can Vitamin E help with scars?
Yes, Vitamin E is often used in skincare products to reduce the appearance of scars. It helps in the healing process and can make scars less noticeable over time.
2. Is it safe to take Vitamin E supplements daily?
While Vitamin E supplements can be beneficial, it’s important not to exceed the recommended dose. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement.
3. Can Vitamin E improve hair health?
Yes, Vitamin E can improve hair health by promoting circulation to the scalp and helping maintain healthy hair growth.
4. What foods are highest in Vitamin E?
Nuts, seeds, vegetable oils, and green leafy vegetables are some of the best sources of Vitamin E.